| Function block | MC_MoveRelative | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Commands a controlled motion of a specified distance relative to the current set position. The relative distance is added to the current set position at the time this command is called. | |||
| VAR_IN_OUT | |||
| B | AxisIn | AXIS_REF | Reference to an axis. |
| VAR_INPUT | |||
| B | Execute | BOOL | Starts the motion at rising edge. |
| E | ContinuousUpdate | BOOL | If TRUE, when the function block (FB) is running and the values of the parameters are updated, the FB will use the new value. If FALSE, the FB won't use the new value. |
| B | Distance | LREAL | Relative distance for the motion [unit]. |
| B | Velocity | LREAL | Value of the maximum velocity. (not necessarily reached) [unit/second] |
| E | Acceleration | LREAL | Value of the acceleration. The unit is determined by MC_ProfileType. (increasing energy of the motor) [unit/second2] or [second] |
| E | Deceleration | LREAL | Value of the deceleration. The unit is determined by MC_ProfileType. (decreasing energy of the motor) [unit/second2] or [second] |
| E | Jerk | LREAL | Value of the jerk. The unit is determined by MC_ProfileType. [unit/second3] or [second] |
| E | BufferMode | MC_BufferMode | Defines how to blend the velocity of two function blocks. |
| VAR_OUTPUT | |||
| B | Done | BOOL | Commanded distance reached. |
| E | Busy | BOOL | The function block is not finished and new output values are to be expected. |
| E | Active | BOOL | The function block is controlling the axis. |
| E | CommandAborted | BOOL | The command is aborted by another command. |
| B | Error | BOOL | Signals that an error has occurred within the function block. |
| E | ErrorID | MC_Error | Error identification. |
|
|||
| MC_MoveRelative | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AXIS_REF | AxisIn | Axis | AXIS_REF | |||
| BOOL | Execute | Done | BOOL | |||
| BOOL | ContinuousUpdate | Busy | BOOL | |||
| LREAL | Distance | Active | BOOL | |||
| LREAL | Velocity | CommandAborted | BOOL | |||
| LREAL | Acceleration | Error | BOOL | |||
| LREAL | Deceleration | ErrorID | MC_Error | |||
| LREAL | Jerk | |||||
| MC_BufferMode | BufferMode | |||||
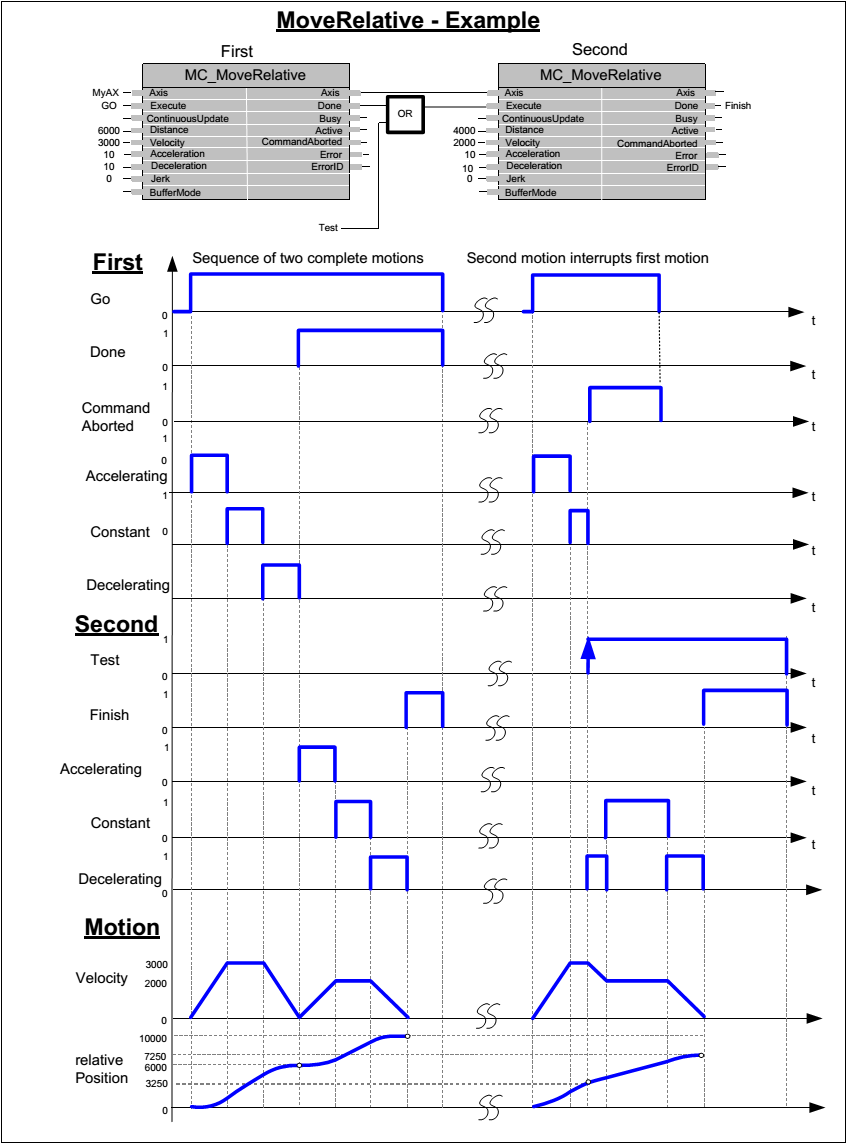
The following figure shows the example of the combination of two relative move function blocks:
- The left part of the timing diagram illustrates the case if the Second function block (FB) is called after the First one. If First reaches the commanded distance 6000 (and the velocity is 0), then the output Done causes the Second FB to move the commanded distance 4000 and moves the axis to the resulting position of 10000.
- The right part of the timing diagram illustrates the case if the Second move function block (FB) starts the execution while the First FB is still executing. In this case the First motion is interrupted and aborted by the Test signal during the constant velocity of the First FB. The Second FB adds the distance 4000 to the set position of 3250 and moves the axis to the resulting position of 7250.